Education

What Is CBD?
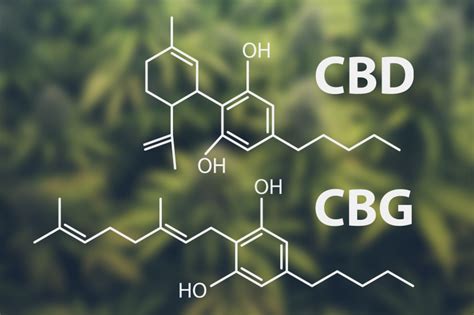
Cannabidiol (CBD) is one of the leading compounds found in hemp; it makes up about 40 percent of hemp’s composition. It’s a non-intoxicating phytocannabinoid – meaning it’s a plant-synthesized chemical that cannot produce a “high” or euphoric feeling. CBD molecules work with our bodies’ endocannabinoid system (ECS) by binding or communicating with CB2 cannabinoid receptors. These special connectors attach to our peripheral nervous system and help regulate various physiological functions with muscles, immune cells, skin, and other organs.
What Is CBG?
Cannabigerol (CBG) is another non-intoxicating phytocannabinoid. While it’s probably the most unusual hemp extract currently, it has a central role in the development of CBD and other known cannabinoids. CBG is regularly referred to as a “mother cannabinoid”; this is because it is the first phytocannabinoid synthesized in hemp that converts into other plant-based cannabinoids. The compound starts in its 2-carboxylic acid form called cannabigerol acid (CBGA). As hemp matures, this component begins to convert into three others: tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA), cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), and cannabichromenic acid (CBCA).
After the conversion, there’s only a small amount of CBGA left – less than one percent. And when hemp begins its decarboxylation process, all those compounds drop their carboxyl acid and become the cannabinoids we commonly recognize: THC, CBD, CBC, and CBG. Because a mature hemp plant contains low levels of CBG, its extraction requires much more effort compared to CBD. Cultivators would either need to harvest hemp before it fully matures, or grow enough hemp plants to yield a significant CBG during the extraction process. And since there is less CBG to go around, research about this particular cannabinoid is limited; however, similar to CBD, CBG also works by attaching to the receptors that make up the endocannabinoid system. In comparison, CBG can bind to both CB1 and CB2 receptors rather than one over the other.

Which Is Better For You?
The results from using CBD, CBG, and other cannabinoids can vary based on our body types, lifestyle, and other physical qualities. And because these two particular cannabinoids work best together than individually, it’s better to figure out which one closest fits your needs or use when comparing CBG vs CBD. They both naturally occur in Cannabis sativa and share some of the same characteristics. However, they are still different in composition and offer unique benefits based on limited research. If you want to learn more about the potential benefits of CBG, CBC, and other cannabinoids, check our educational blogs for more information about non-CBD cannabinoids. And after becoming more knowledgeable about CBG vs CBD vs CBC’s differences, the more confident you’ll be with purchasing CBD or hemp-based products that best suit your needs and achieve personal goals.
